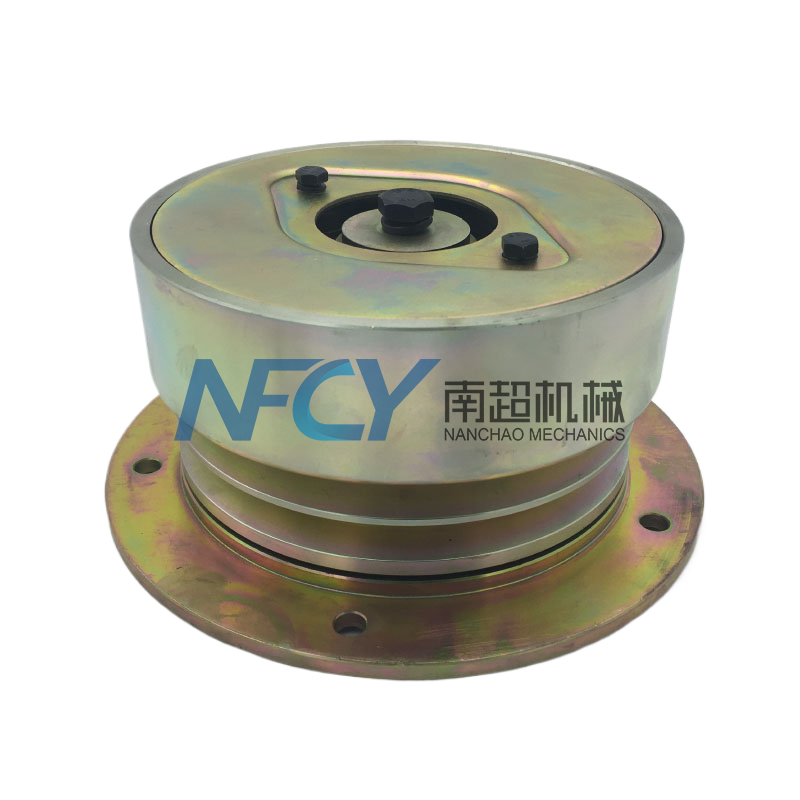
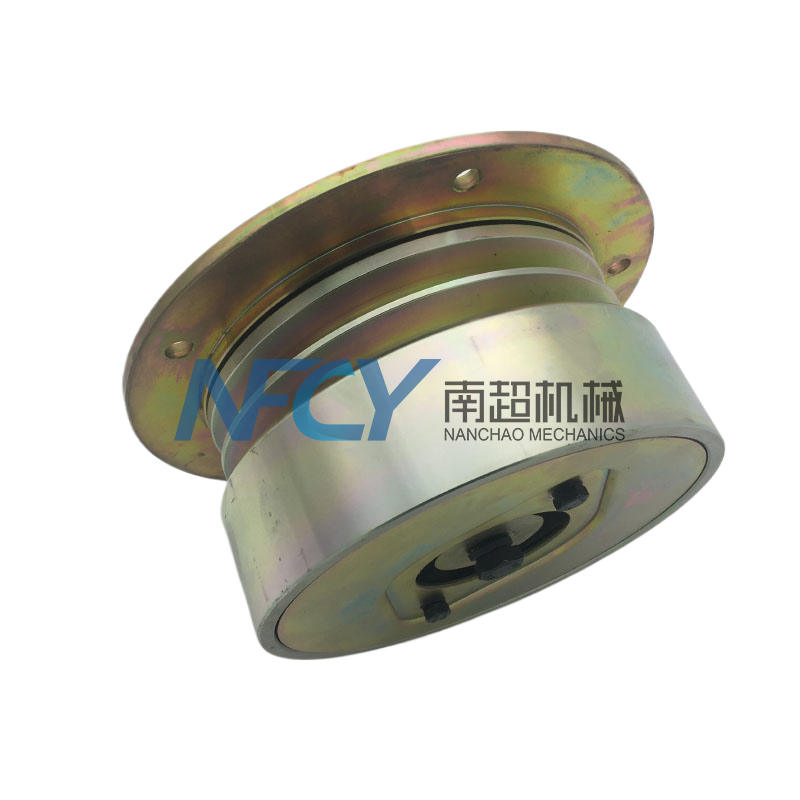
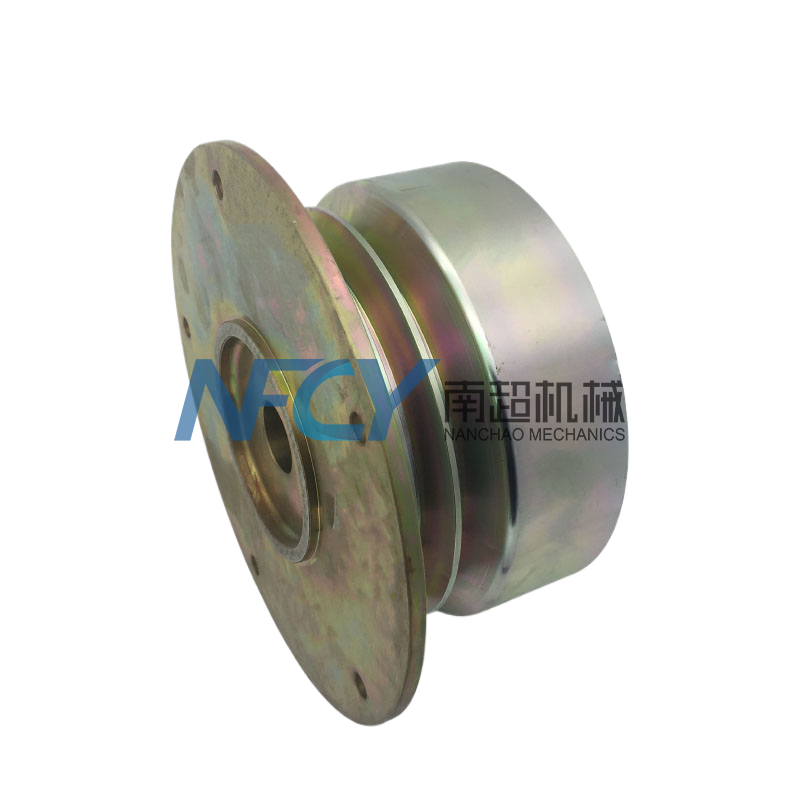
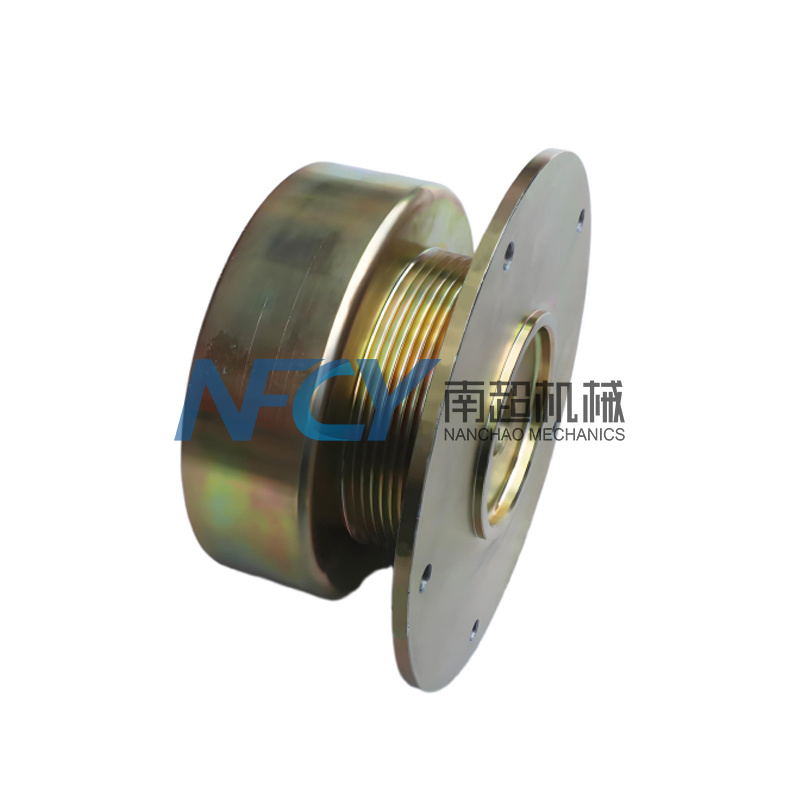
Coupling
- Commodity name: Coupling
Product Description
Elastic Pin Coupling
The two halves of the coupling are connected by elastic pins, featuring a simple structure and strong compensation capacity.
Structure
It is composed of two half couplings, elastic pins and bolts, etc.
Working principle
When the coupling is in operation, the pins can freely extend and retract in the flange holes of the two halves of the coupling to compensate for the relative displacement of the two shafts and at the same time play a role in buffering and vibration reduction. When axial, radial or angular displacements occur between the two shafts, the elastic pin will undergo elastic deformation, thereby absorbing these displacements and ensuring the stable transmission of torque.
Characteristics
The structure is simple, manufacturing is convenient, and it is easy to install, disassemble and replace the elastic elements
Plum Blossom-shaped Elastic Coupling
It is mainly composed of two half couplings with the same convex claw shape and an elastic element. The elastic element is generally in the shape of a plum blossom and is placed between the convex claws of the two half couplings. The power is transmitted through the squeezing between the convex claws and the elastic element. When there is a relative offset between the two axes, the elastic element undergoes corresponding elastic deformation, playing an automatic compensation role, thereby achieving the effect of vibration reduction and buffering.
Characteristics
Reliable performance, compact structure, strong compensation capacity, durable components and convenient maintenance
Diaphragm Coupling
The diaphragm coupling is a high-performance mechanical transmission component. It compensates for the relative displacement of two shafts by the elastic deformation of the diaphragm. It has the advantages of high precision, high torque rigidity, zero-clearance transmission, and corrosion resistance, and is widely used in industrial automation.
Structure
It is composed of two sets of metal diaphragms, an intermediate shaft sleeve and connecting bolts. Diaphragms are usually made of stainless steel or alloy steel and are rigidly connected to the half couplings at both ends by bolts.
Working principle
Displacement compensation is achieved through the elastic deformation of the diaphragm. When axial, radial or angular deviations occur between the two shafts, the diaphragm bends or twists, thereby absorbing the deviations and maintaining the continuity of torque transmission.
Characteristics
High-precision transmission, high-torque rigidity, maintenance-free design, corrosion and high-temperature resistance, vibration and noise suppression
Key words:
Coupling
What Else Might You Learn?